High Bandwidth Memory – all servers use memory (DRAM) with DIMMs containing memory chips, connecting to the CPU across the memory bus. DDR4 DIMM capacity is up to 256GB and the data rate is up to 50GB/sec. HBM is a way of getting more bandwidth from a DRAM package by stacking memory dice one above the other. They are interconnected, using TSV (Through Silicon Via) technology, to a logic die which uses an interposer to connect them to a CPU or GPU.
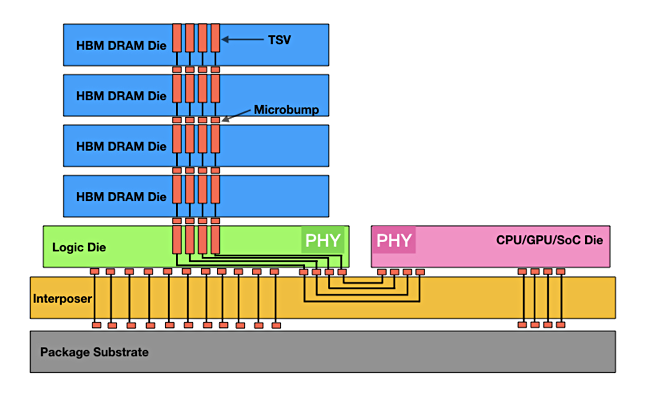
Think of HBM as a different way of combining memory chips and giving them closer and faster access to the CPU. The distance to the processor is only a few ㎛ units which helps speed data transfers. HBM has developed across generations with HBM1, then generations 1 and 2 HBM2, HBM2 Extended (HBM2E), HBM3 gen 1, gen 2 and extended and the coming HBM4 and HBM4e.
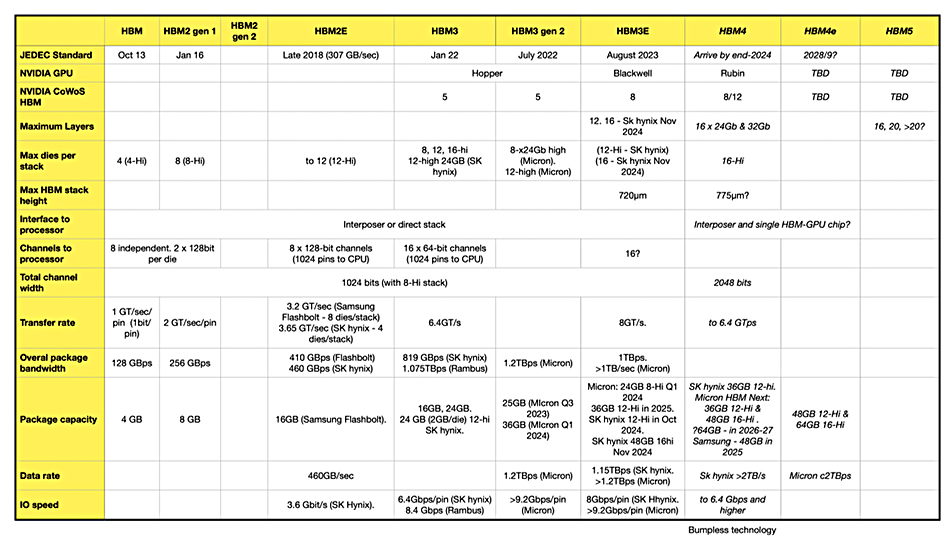
HBM3 was specified by JEDEC in January 2022 and vendors promptly started extending it with so-called Gen 2 products coming from Micron in July 2022. SK hynix introduced samples of its HBM3E (HBM third generation Extended) in August 2023 in advance of any forthcoming JEDEC standard.
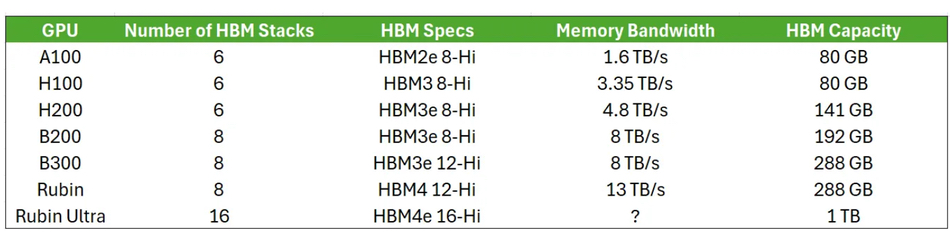
Moore Morris and Ray Wang write: “With each generation of AI chip, an upgrade in HBM is a key factor for better performances (higher bandwidth or capacity). In a tick-tock cycle, the main upgrade for NVIDIA GPU in its 2nd generation of the same architecture will be the HBM capacity. 50% jump in HBM capacity from H100 to H200, B200 to B300 and 4x jump from Rubin to Rubin Ultra.”